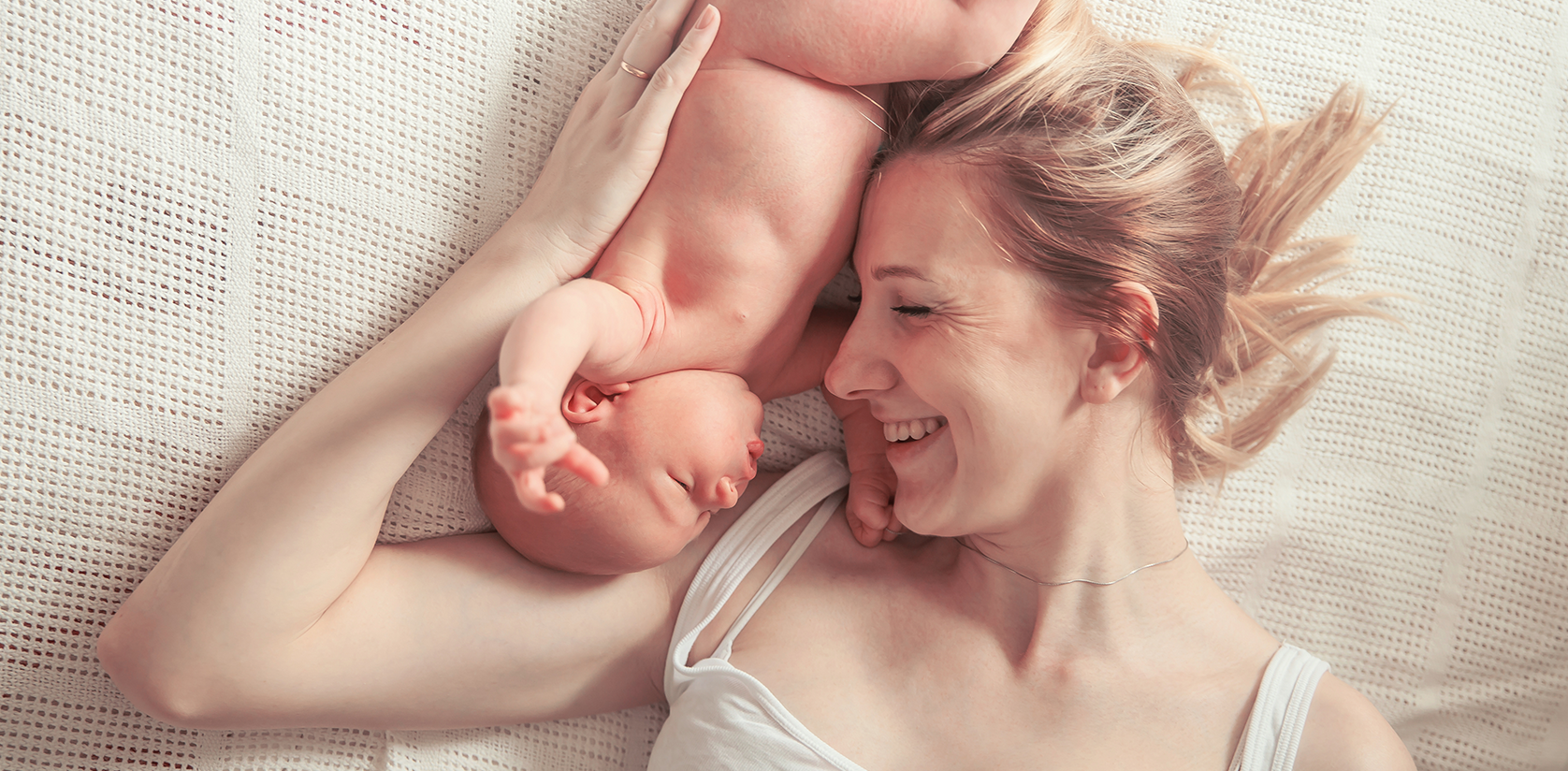

Navigating the complete pregnancy journey
Your trimester guide detailed
The body undergoes profound physiological and anatomical changes, requiring prenatal nutrition plans and sleep hygiene to support fetal growth. Hormonal shifts influence energy levels significantly throughout gestational trimesters, while obstetric scans ensure optimal maternal wellness and fetus safety. Expectant mothers experience heightened sensory perception and emotional variations. Daily habits shift to accommodate the physical demands of labor preparation and postpartum recovery.
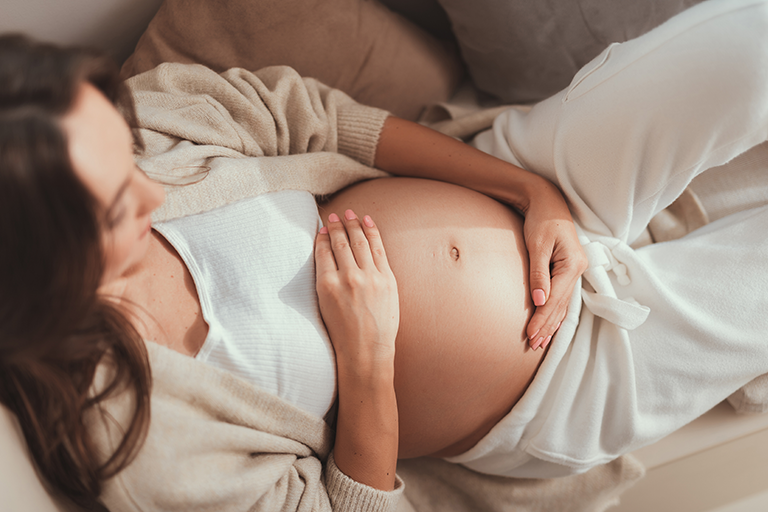

A
Strategic preparations for postpartum care
Nesting checklist active


Designing the safe nursery
Selecting a bassinet with approved safety standards forms the foundation of safe sleep guidelines. Blackout curtains assist in establishing circadian rhythms early on, while a changing station organized with essential hygiene products streamlines late-night care. Dimmable nightlights allow parents to check on the sleeping baby without disrupting their rest cycles.

Packing the maternity hospital bag
Essentials include loose maternity wear, nursing bras, and hygiene kits to assist with immediate postpartum recovery. Documents such as administrative paperwork and the birth plan must be easily accessible to ensure a smooth admission process. Snacks and hydration sources provide necessary energy for the birthing partner during the long hours of labor support.



Babyproofing safety measures
Anchoring heavy furniture prevents tipping accidents once the infant becomes mobile and starts pulling up. Installing carbon monoxide alarms and securing electrical outlets with socket protectors creates a protected space for exploration. Hazardous toxic substances require storage in high cabinets or locked drawers to prevent accidental ingestion by curious toddlers.
Building a postpartum support network
Mental load shared
Tracking infant developmental milestones
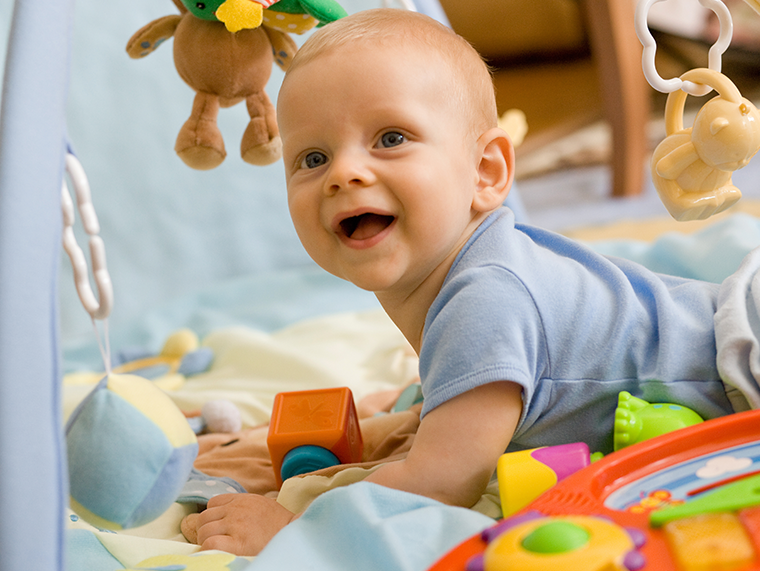

Gross motor skills
Infants initially develop neck control before gradually mastering the core strength required for rolling over and sitting upright. Regular tummy time sessions actively encourage muscle development, paving the way for gross motor milestones like crawling. Fine motor coordination evolves later, allowing the child to utilize the pincer grasp, manipulate toys, and eventually feed themselves confidently.
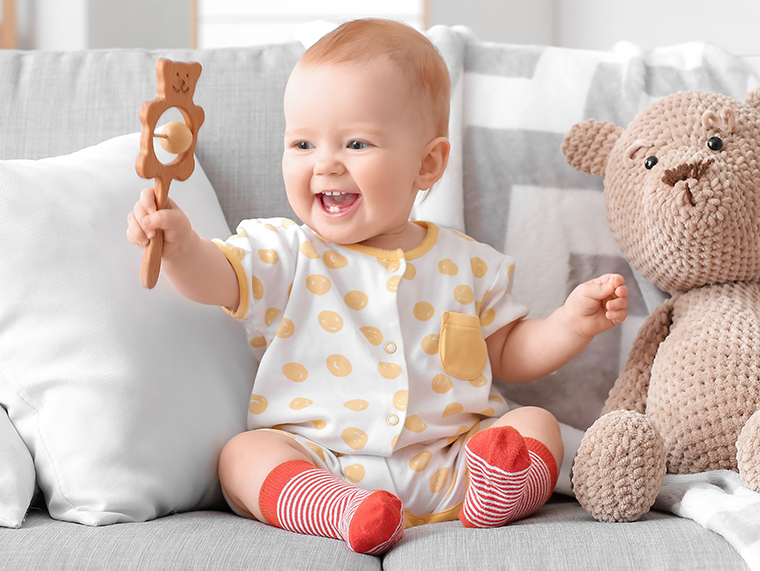

Sensory processing growth
Early recognition of faces and high-contrast cards signals the awakening of visual processing centers. Cause-and-effect reasoning emerges when babies realize that shaking a rattle produces sound, marking a leap in intellectual engagement. Object permanence improves gradually, enabling the child to find hidden toys and recognize familiar daily routines or sequences.

Social and secure attachment
The first social smile usually appears around six weeks, indicating a deliberate response to human interaction. Separation anxiety demonstrates the establishment of secure attachment and deep emotional bonds with caregivers. Interactive bonding builds early empathy and teaches the fundamental concepts of co-regulation, sharing, and taking turns with others.
G
Prioritizing pediatric health protocols
Vaccination schedule routine




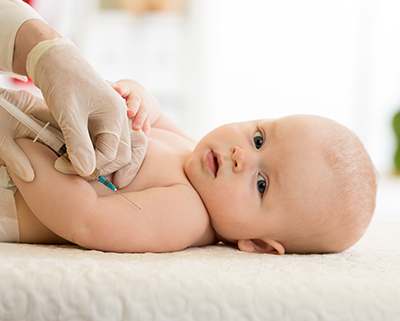


Feeding and Immunity
Breastfeeding or infant formula provides the essential antibodies and macronutrients required for rapid brain expansion. Introducing solids around six months exposes the palate to diverse textures and reduces potential common allergens through gradual exposure. Iron-fortified foods support blood volume increase as the infant grows rapidly during these formative months.